Design Patterns
A lecture note for exam revision.
1. Strategy
1.1 Intent
To define a family of algorithms, put each of them into a separate class, and make their objects interchangeable.
1.2 Problem
- Have alternative versions of an algorithm
- Want to switch between them at runtime
Using switch statement in one class makes the class too complex.
1.3 Solution
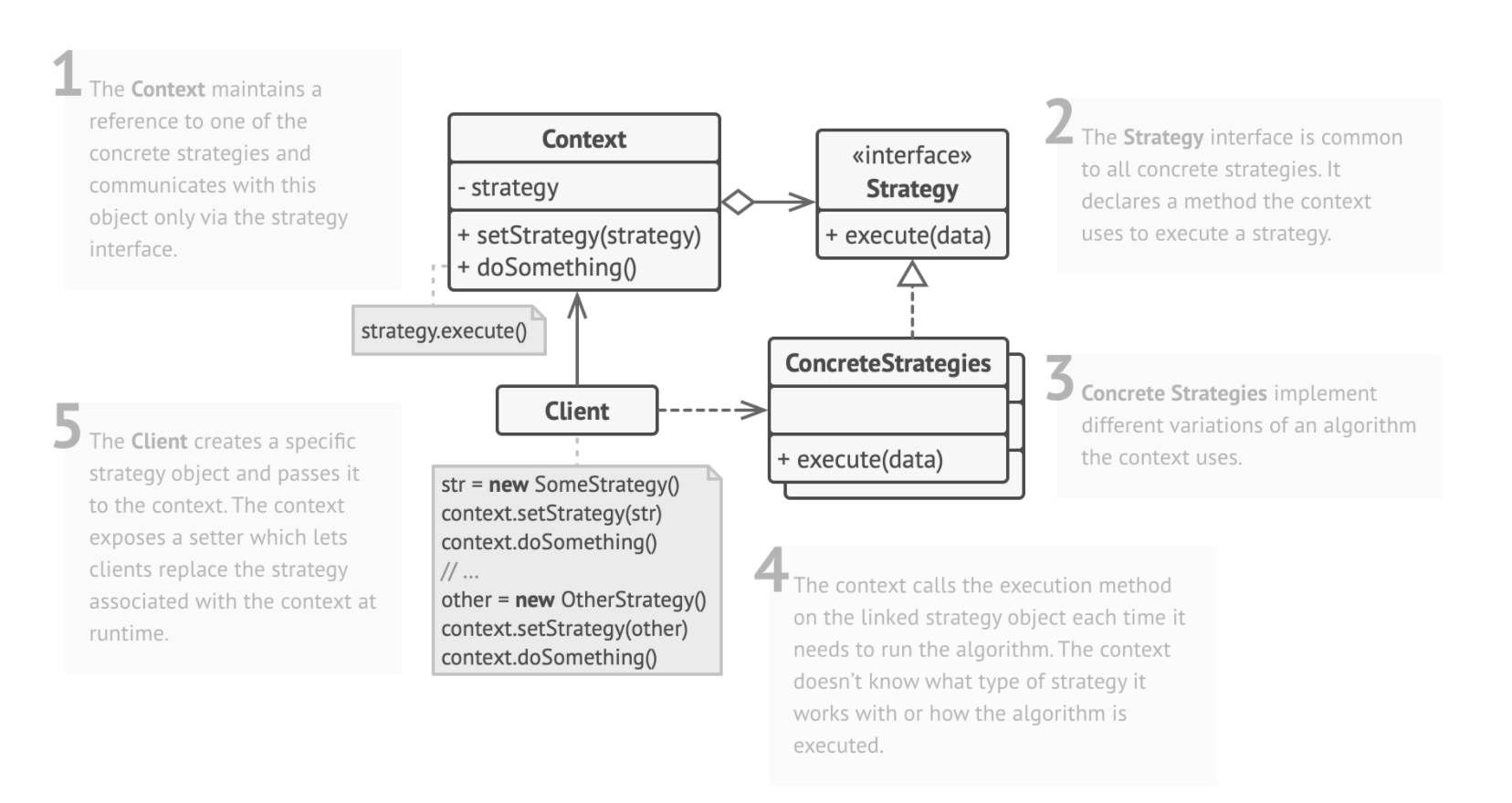
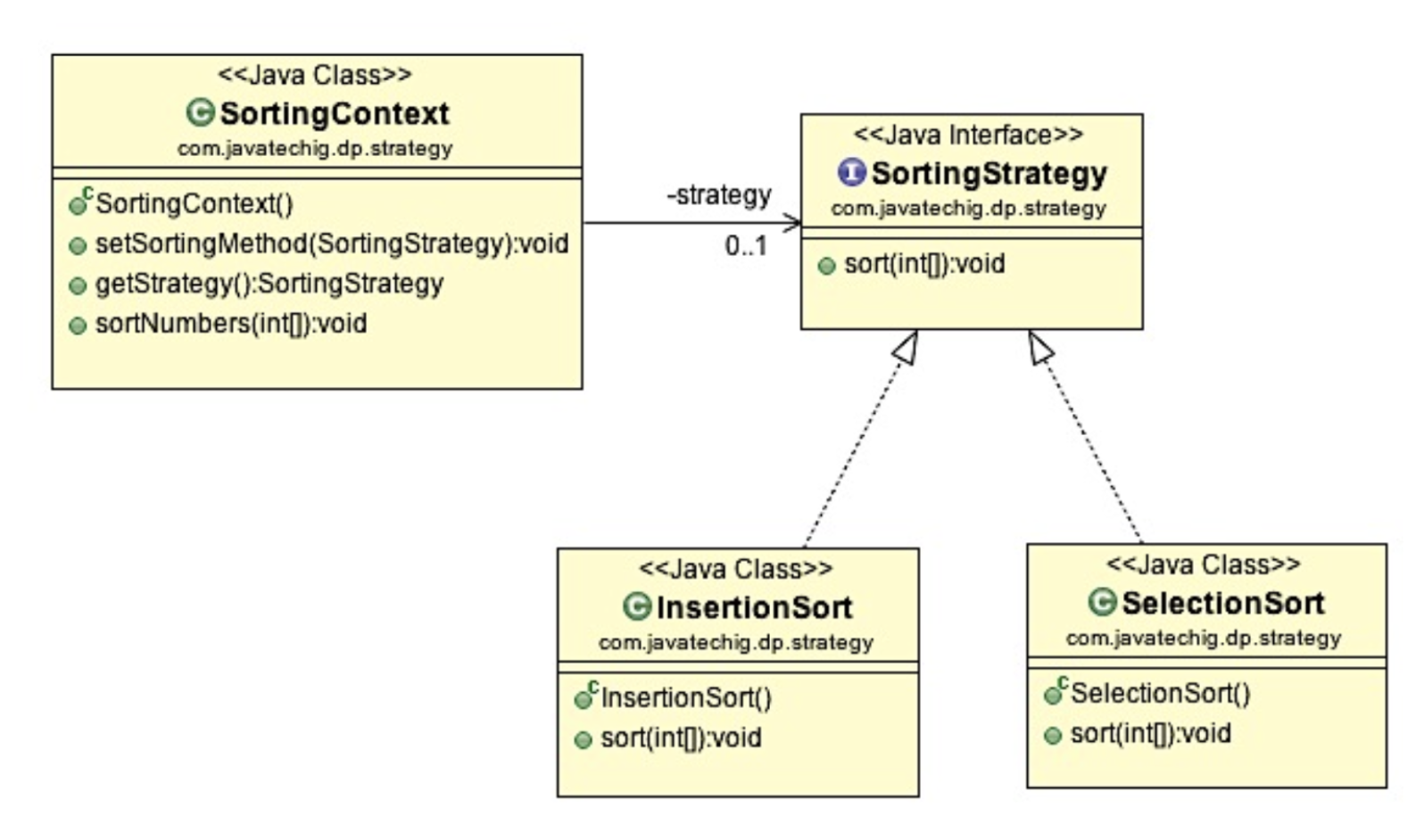
Use separate classes to implement different version of the algorithm. These classes are called strategies.
The original class, called context, has a field for storing a reference to one of the strategies. The context delegates the work to a linked strategy object instead of executing it on its own.
2. State
2.1 Intent
To let an object alter its behavior when its internal state changes during runtime. It appears as if the object changed its class.
2.2 Problem
- Have object that needs to change its behavior at runtime, based on its state
Using if or switch statements, again, will make the class complex, and if more states need to be added, the whole class needs to be modified.
2.3 Solution
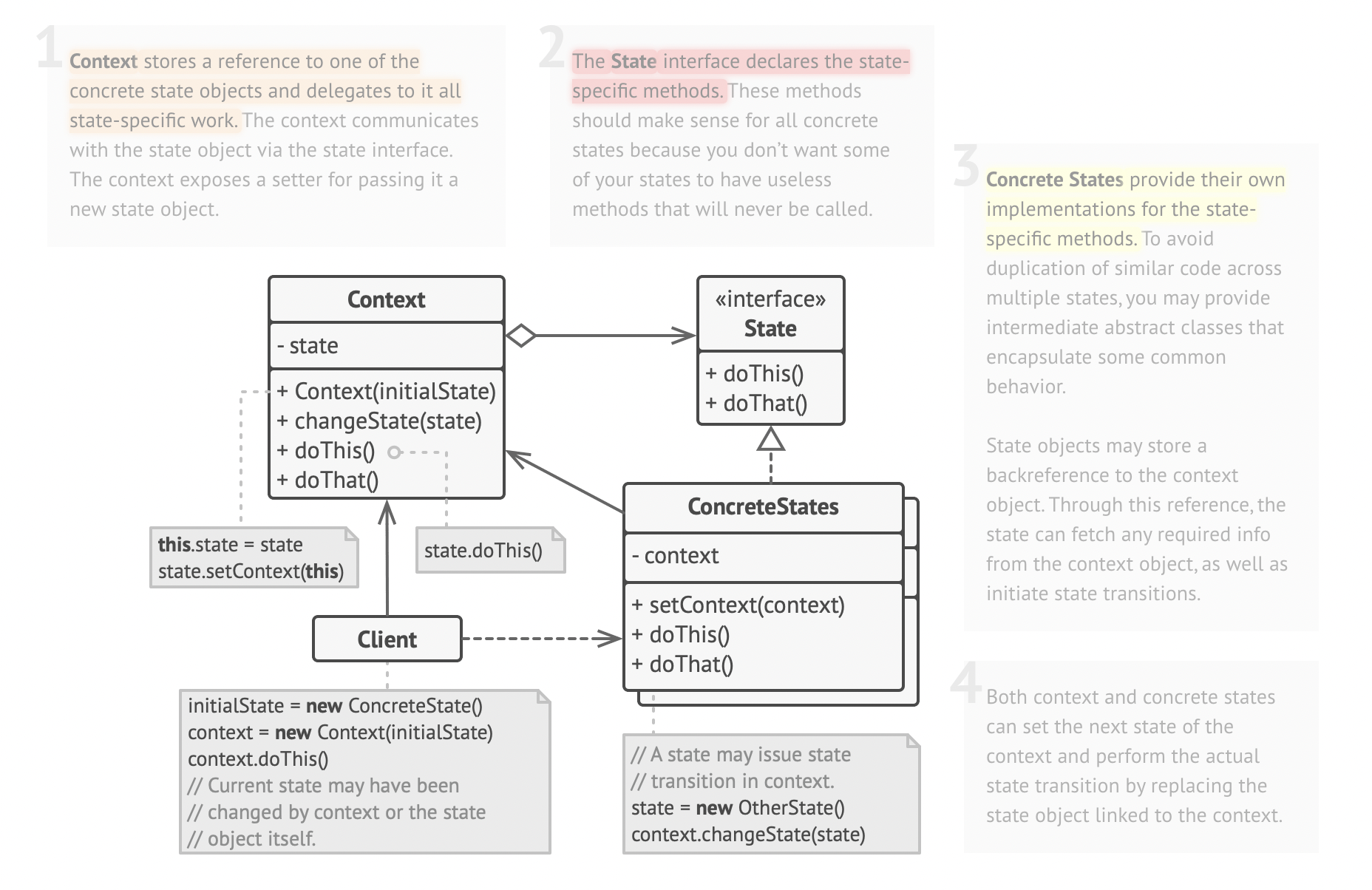
Create new classes for all possible states of an object and extract all state-specific behaviors into these classes.
The original object, called context, stores a reference to one of the state objects that represents its current state, and delegates all the state-related work to that object.
2.4 Strategy vs State
Both are behavioral patterns;
Strategy: alternative algorithms, one class per algorithm; client pick one algorithm to use via the common strategy interface;
State: different state/role of the same object, one class per state; client pick one state to use via the common object interface.
In State pattern, the particular states may be aware of each other and initiate transitions from one state to another, whereas strategies almost never know about each other.
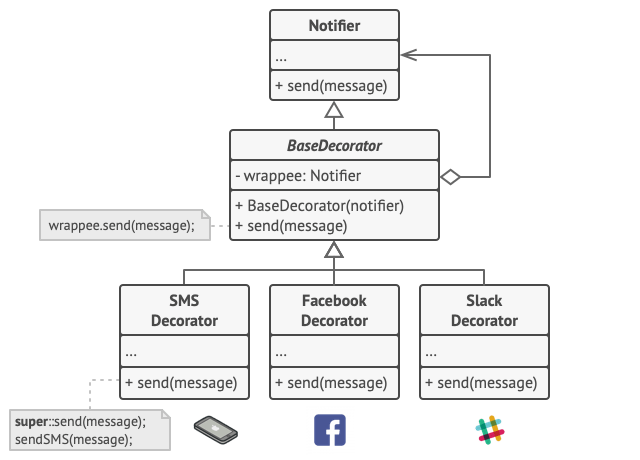
3. Decorater
3.1 Intent
To attach new behaviors to objects by placing these objects inside special wrapper objects that contain the behaviors.
3.2 Problem
- Add additional feature to an object without using complex multiple inheritance.
3.3 Solution
Use a decorator (or can be called as a wrapper) to ‘enhance’ the object.
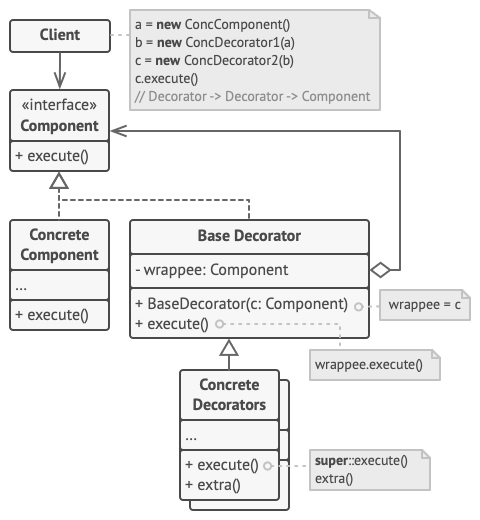
A wrapper is an object that can be linked with some target object. The wrapper contains the same set of methods as the target and delegates to it all requests it receives. However, the wrapper may alter the result by doing something either before or after it passes the request to the target, and this is where the ‘enhancement’ comes from.
Client code be like:
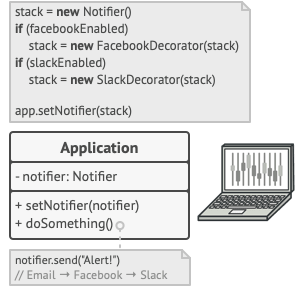
Another example (from the slides):

4. Composite
4.1 Intent
To compose objects into tree structures and then work with these structures as if they were individual objects.
4.2 Problem
- How to treat individual objects and their compositions uniformly
Only makes sense when the core model structures like a tree.
4.3 Solution
Work with composite components and leaf components in a unified way, say, through a common interface.
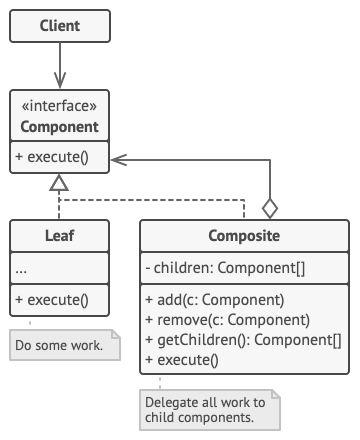
Four participants:
- Component: defines the common interface for both simple(individual/primitive) and complex(composite) elements in the tree.
- Leaf: defines behavior for primitive objects in the composition. Serves as ‘basic’ or ‘simple’ elements in the tree. Doesn’t have sub-elements.
- Composite: or a container, has sub-elements: leaves or other composites(containers). Stores a list of child elements (both primitive objects and composite objects). Implements child/structure related operations (add child, remove child, get children, etc).
- Client: works with all elements via component interface, in a unified way with both simple and complex elements.
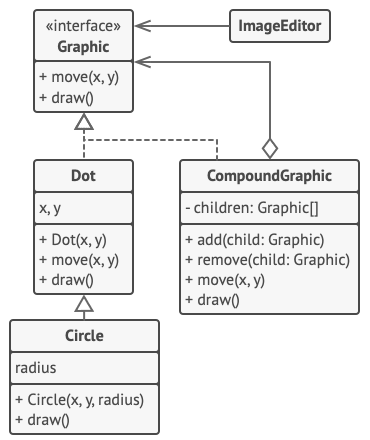
4.4 Composite vs Decorator
Both are structural patterns.
Difference:
Composite is for object composition: composes multiple objects into a single one.
Decorator is for function/feature extension: adds additional features to a leaf object.
Decorator adds additional responsibilities to the wrapped object
Composite just “sums up” its children’s results.
5. Observer
5.1 Intent
Create a subscription mechanism to notify multiple objects about any events that happen to the object they’re observing.
5.2 Solution
Two main components:
- Observer: the object that watches on the state of another object. Provides a method for the subject to notify any changes; provides a method to set a subject to observe.
- Subject: the object that is being watched. Provides method for an observer objet to register and unregister; has a method to notify all observers.

5.3 Publisher - Subscriber
Publisher-Subscriber pattern is a specific implementation of Observer pattern where:
Publisher = Subject
- Stores a list of subscribers
- Provides a method for subscribers(observers) to register/unregister
- Provides a method to notify all subscribers(observers)
Subscriber = Observer
- Provides a method to get notified
- Provides a method to register with the publisher
6. Mediator
7. Iterator
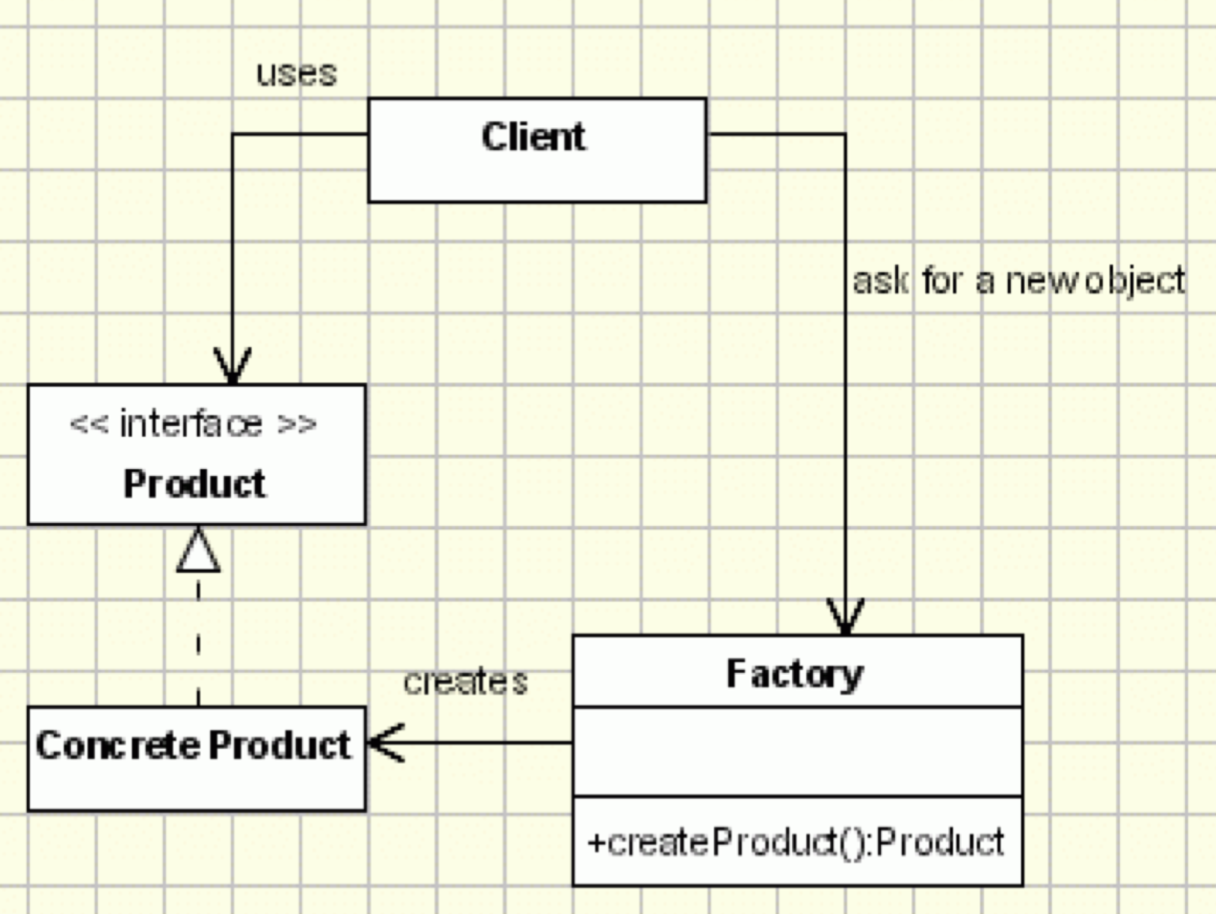
8. Factory
8.1 Intent
To create objects without exposing the instantiation logic to the client program.
8.2 Solution
Implementation
- Define a Factory Class that implements the object creation logic for a Concrete Product class.
- Define a Product class whose objects are to be created by the Factory class.
- Define a Client class that uses the Factory class to create objects.
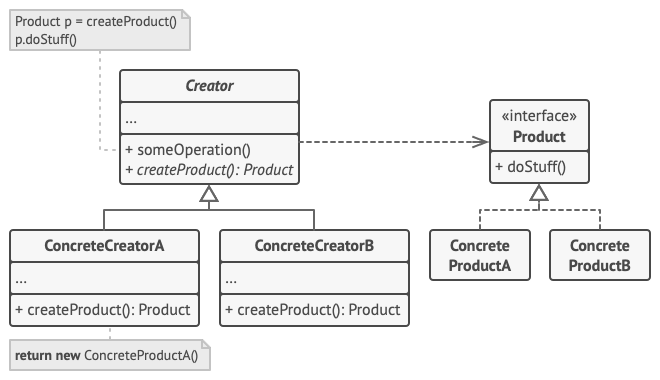
9. Factory Method
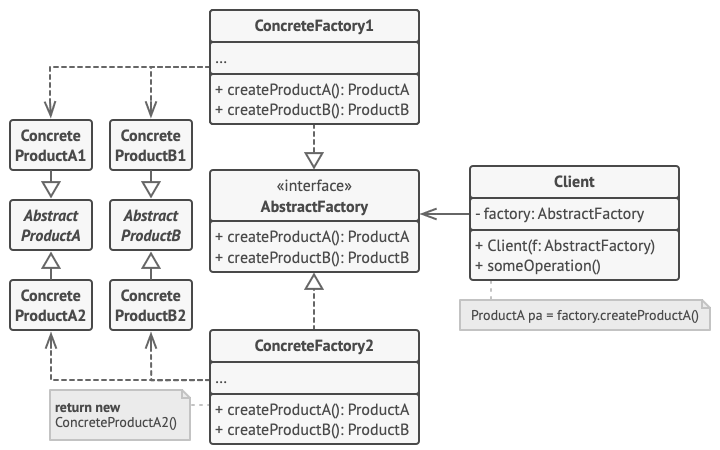
10. Abstract Factory
— Jun 2, 2022